Category: Industry Information
Date: 2018-07-06
Click: 4398
Author: admin
Collection:
Lithium Grid News: Recently, PNNL of the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory released a heavy news on its official website. The final capacity retention rate of the cycle is only 100 times.
Lithium Grid News: Recently, PNNL of the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory released a heavy news on its official website. According to the report, PNNL has developed a high-performance lithium metal battery electrolyte that can increase the service life of lithium metal batteries by 7 times. Above, PNNL stated that the project is part of the “Battery500 consortium” program, which aims to develop a lithium battery with a high reliability, long life and low cost that is more than three times the energy of current lithium-ion batteries , so that the specific energy of the battery pack can be achieved. 500Wh/kg or more. But many domestic media puts interpreted as "PNNL developed an electrolyte, so that the battery life increased 7 times", did not mention the metal lithium battery, apparently suspected of misleading readers.

The theoretical specific capacity of the metal lithium electrode reaches 3860 mAh/g, and the potential is only -3.04 V (vs standard hydrogen electrode), which is a very ideal anode material , but the metal lithium anode has a fatal defect - metallic lithium dendrites. In order to solve the problem of lithium dendrites, various solutions have been proposed. Electrolyte optimization is a common method by adding some F-containing compounds to the electrolyte, such as (C2H5)4NF(HF)4, fluoroethylene carbonate. Ester and the like can significantly improve the stability of the SEI film on the surface of the metal Li. High concentration of Li salt has also proven to be a very effective method. For example, a high concentration of LiTFSI electrolyte can significantly inhibit the growth of lithium dendrites in Li-S batteries. . Although a high concentration electrolyte is beneficial to improve the performance of the metal Li negative electrode, it also has a negative effect, such as an increase in viscosity of the electrolyte, a decrease in ionic conductivity, and an increase in the cost of the electrolyte.
Recently, Shuru Chen et al. of PNNL of the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory proposed a partial dilution solution, that is, adding a partially electrochemically stable diluent to a high concentration electrolyte, and the Li salt in the electrolyte will not dissolve. Among these diluents, but the solvent in the high-concentration electrolyte can dissolve with the diluent, so the "diluted" electrolyte will form a local high concentration zone and a local low concentration zone, thereby retaining a high concentration. In the case of the excellent characteristics of the electrolytic solution, the problem of the high concentration electrolyte solution is solved. Under the guidance of this concept, Shuru Chen et al. designed an electrolyte that works stably in a metal Li negative electrode and a 4V positive electrode system, which suppresses the growth of the negative Li dendrites and the cycle life of the metal Li/NCM111 battery. It has been improved by more than 7 times, greatly improving the practicality of the metal Li battery.
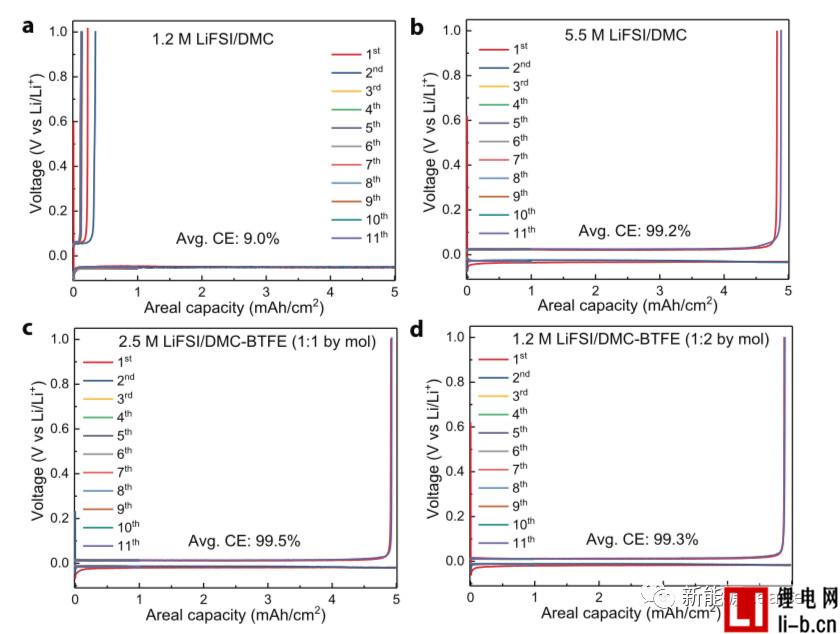
In the experiment, Shuru Chen used bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)ether (BTFE) to dilute the 5.5M LiFSI/DMC electrolyte to obtain a partially diluted electrolyte with different LiFSI concentrations. The following figure shows the Coulomb efficiency comparison chart of different electrolyte Li/Cu batteries. It can be seen from the figure that the coulombic efficiency of 1.2M LiFSI/DMC electrolyte is very low, only about 9%. If the LiFSI concentration is increased to 5.5M The coulombic efficiency of the battery is immediately increased to 99.2%. It can be seen that the high concentration of LiFSI electrolyte has a significant effect on improving the performance of the metal Li negative electrode. When a portion of the BTFE was added to the electrolyte, even a reduction in the concentration of LiFSI to 2.5M and 1.2M maintained a high coulombic efficiency (99.5% and 99.2%, respectively), indicating that the partially diluted electrolyte was It has a significant effect on inhibiting the growth of Li dendrites and improving the coulombic efficiency.
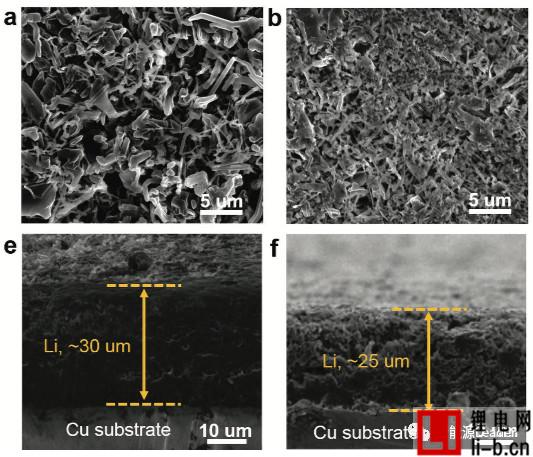
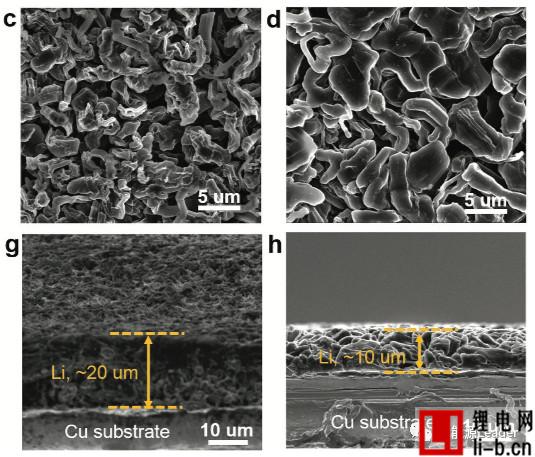
The figure below shows the SEM picture of the electrode after different electrolyte cycles (Fig. a, e is the traditional LiPF6 electrolyte, Fig. b, f is 1.2M LiFSI/DMC, Fig. c, g is 5.5M LiFSI/DMC electrolyte, figure d, h is 1.2M LiFSI/DMC-BTFE electrolyte), we can see from the figure that in the traditional LiPF6 electrolyte and 1.2M LiFSI electrolyte, the metal Li exhibits a loose and porous state, accompanied by Li The growth of dendrites, but in the electrode of the partially diluted electrolyte 1.2M LiFSI/DMC-BTFE, we can observe that it consists mainly of Li particles with a diameter of about 5 μm, without the growth of Li dendrites. From the cross-section of these electrodes, we can also see the effect of different electrolytes on the metal Li anode. The thickness of the electrode in the 1.2M LiFSI/DMC-BTFE electrolyte is significantly lower than that in the other electrolyte. The same), which indicates that the metal Li anode can form a denser structure in the partially diluted electrolyte, thereby reducing the occurrence of side reactions and improving coulombic efficiency and cycle life.

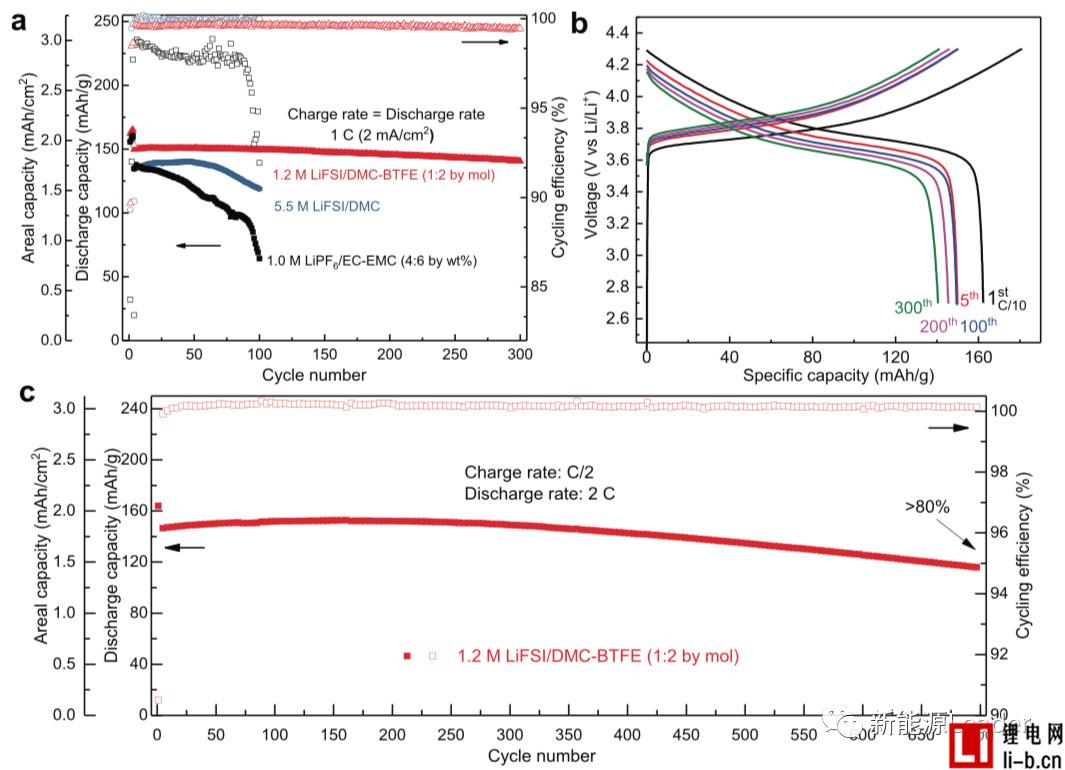
In order to verify the stability of the above electrolyte in a high voltage system, Shuru Chen uses a metal Li as a negative electrode and a NMC111 material as a positive electrode (2 mAh/cm2, 4.3 V). The following figure shows a full battery using different electrolytes. Electrochemical performance. From Fig. a, we can see that under the 1C charge-discharge rate, the battery with the traditional electrolyte has a phenomenon of rapid polarization increase and rapid decline of life (100 cycles, capacity retention rate is only 40%). Although the high concentration of 5.5M LiFSI/DMC electrolyte has some help to improve the coulombic efficiency of the metal Li anode, there is still a continuous increase in polarization and capacity decay in the cycle. The final capacity retention rate of the cycle is only 100 times. About 76%, this may be caused by an excessively high Li salt concentration resulting in an increase in electrolyte viscosity, a decrease in ionic conductivity, and a decrease in wettability. The partially diluted electrolyte exhibited excellent cycle performance in the cycle (300 cycles, capacity retention rate of about 95%, and cycle capacity retention rate of >80%).
According to the research on the mechanism of action of the above electrolyte, the force between LiFSI and BTFE is significantly weaker than that between LiFSI and DMC. Therefore, LiFSI is more prone to solvation of DMC, which is formed in the electrolyte. The local high concentration LiFSI-DMC region guarantees the performance of the metal Li battery. In addition, the addition of a portion of BTFE to a high concentration of LiFSI-DMC can improve the diffusion capacity of Li+ and reduce the diffusion capacity of FSI-, thereby improving the rate performance of the electrolyte. The frontier orbital theoretical calculation also shows that FSI- will decompose on the surface of the negative electrode before DMC, thereby producing a SEI film with higher LiF content, thereby stabilizing the interface between the metal Li negative electrode and the electrolyte, and improving the cycle stability of the metal Li battery.
From a unique perspective, ShuruChen et al. retained a local high-concentration Li salt region in a low-concentration electrolyte by a partial dilution method. This has the advantage of not only maintaining a high concentration of Li salt in inhibiting the growth of Li dendrites. Improve the efficiency of the lithium-ion battery coulombic efficiency, and avoid the disadvantages of high-concentration electrolyte high viscosity, low ionic conductivity, and high cost, achieving the significant result of the stable circulation of Li/NMC battery 700 times, for the development of high ratio It is of great significance to be able to increase the cruising range of electric vehicles with metal Li batteries .



 Online map
Online map Collection Website
Collection Website





